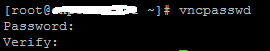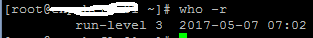On a newly created RHEL VM/EC2 instance graphical interface is not normally configured.
In the below blog, we will discuss about configuring the VNC server on a RHEL machine.
XRDP configuration is discussed at the end of this blog post.
Elevate your user with root privileges.
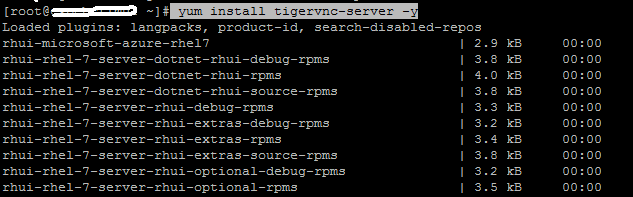
Install the required packages using below command:
yum install tigervnc-server -y
Set VNC password for the client sessions
vncpasswd
Make a note of password used.
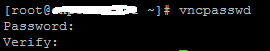
Start a VNC session.
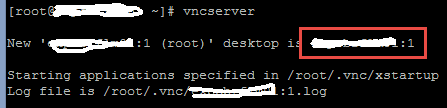
Note that you session number is 1.
Now to try to connect to your VNC session using a VNC client tool from you windows machine.
VNC uses port 59XX (where XX is the desktop instance number). In above case my instance number will be 5901.
Make sure you have allowed this port on your cloud inbound security rule and also on the Linux firewall.
After these changes, if you get a blank screen when connected to the session, check the run level of your system and follow the below steps:
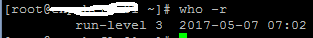
GUI interface is not enabled in run level 3. Switch to run level 5 to enable the GUI mode.

You will need a server reboot for this change to take effect.
check the run level again after the reboot.

Now install the GUI server with the below command:

Once done you should be able to connect to the GUI screen using VNC viewer.
To configure XRDP, perform the below steps:
Download the RPM packages:
# rpm -Uvh http://download.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/x86_64/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
Note: Always use the updated URL.
Install the XRDP packages:
# yum install xrdp -y
Start XRDP service and make it persistent:
#service xrdp start
#chkconfig xrdp on
XRDP uses port 3389.
Make sure you have allowed this port on your cloud inbound security rule and also on the Linux firewall.
Now you should be able to connect to your Linux machine using Microsoft Windows Terminal Services Client (MSTSC) from your windows machine.
Additional Notes for Ubuntu:
If you are not able to connect with XRDP, Execute following commands on Ubuntu:
Install xfce4
#sudo apt-get install xfce4
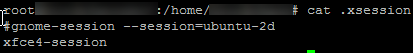
Add following lines to users .xsession file under home directory and comment out the rest of the line.
xfce4-session